SECAM
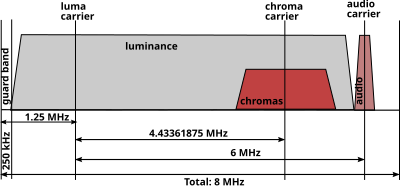
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (French pronunciation: [sekam], système électronique couleur avec mémoire, French for electronic color system with memory), is an analog color television system first used in France. It was one of three major analog color television standards, the others being PAL and NTSC. This page primarily discusses the SECAM colour encoding system. The articles on broadcast television systems and analog television further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation. SECAM video is composite video because the luminance (luma, monochrome image) and chrominance (chroma, color applied to the monochrome image) are transmitted together as one signal.
All the countries using SECAM are currently in the process of conversion, or have already converted to Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB), the new pan-European standard for digital television. SECAM remained a major standard into the 2000s.
Development of SECAM began in 1956 by a team led by Henri de France working at Compagnie Française de Télévision (later bought by Thomson, now Technicolor). The technology was ready by the end of the 1950s, but this was too soon for a wide introduction. A version of SECAM for the French 819-line television standard was devised and tested, but not introduced.[1] Following a pan-European agreement to introduce color TV only in 625 lines, France had to start the conversion by switching over to a 625-line television standard, which happened at the beginning of the 1960s with the introduction of a second network.
The first proposed system was called SECAM I in 1961, followed by other studies to improve compatibility and image quality.
These improvements were called SECAM II and SECAM III, with the latter being presented at the 1965 CCIR General Assembly in Vienna.
Further improvements were SECAM III A followed by SECAM III B, the adopted system for general use in 1967, and first SECAM broadcast was made in France that year.