USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply (interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers.[2] A broad variety of USB hardware exists, including 14 different connector types, of which USB-C is the most recent and the only one not currently deprecated.
First released in 1996, the USB standards are maintained by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). The four generations of USB are: USB 1.x, USB 2.0, USB 3.x, and USB4.[3]
USB was designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to personal computers, both to communicate with and to supply electric power. It has largely replaced interfaces such as serial ports and parallel ports, and has become commonplace on a wide range of devices. Examples of peripherals that are connected via USB include computer keyboards and mice, video cameras, printers, portable media players, mobile (portable) digital telephones, disk drives, and network adapters.
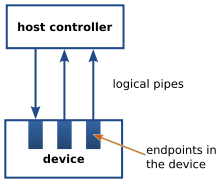
Each USB connection is made using two connectors: a socket (or receptacle) and a plug. In the following table, schematics for only the sockets are shown, although for each there is a corresponding plug (or plugs).
The Universal Serial Bus was developed to simplify and improve the interface between personal computers and peripheral devices, such as cell phones, computer accessories, and monitors, when compared with previously existing standard or ad hoc proprietary interfaces.[4]
The USB standard also provides multiple benefits for hardware manufacturers and software developers, specifically in the relative ease of implementation: