| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
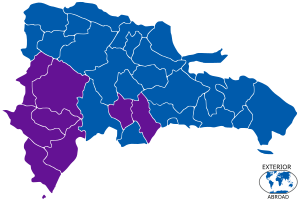 Presidential election result by district | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
Dominican Republic portal
|
General elections were held in the Dominican Republic on 5 July 2020 to elect a president, vice-president, 32 senators and 190 deputies. They had originally been planned for 17 May, but were postponed due to the coronavirus pandemic.[1][2] They are the second elections since 1994 in which all positions will be elected simultaneously, and the first in Dominican history in which all authorities will be elected simultaneously and directly.[3][4][5][6]
Incumbent President Danilo Medina was ineligible to stand for re-election, having served two consecutive terms since 2012. The governing Dominican Liberation Party's 16-year rule ended after Modern Revolutionary Party candidate Luis Abinader received a majority of the vote.[7] Rival candidates Gonzalo Castillo and Leonel Fernández also conceded defeat.[7] The Modern Revolutionary Party also won a majority of seats in the Senate and a plurality in the Chamber of Deputies. The election was a partial realignment, with the Modern Revolutionary Party entering a status as a major party in the country, replacing the Dominican Revolutionary Party, who saw poor election results for the second election in a row and who obtained its lowest total vote share and seat count in its history. Abinader would be officially sworn in as President on August 16.[8]
Electoral system[edit]
The President of the Dominican Republic is elected using the two-round system; if no candidate receives 50% + 1 vote, or more, of the total votes, a second-round runoff will be held between the two candidates with the highest votes on the first round.
The 32 members of the Senate are elected from the 31 provinces and the Distrito Nacional using first-past-the-post voting.[9]
The 190 members of the Chamber of Deputies are elected in three groups; 178 are elected by proportional representation from 32 multi-member constituencies based on the 31 provinces and the Distrito Nacional, with the number of seats based on the population of each province. A further seven members are elected by proportional representation by Dominican expatriates in 3 overseas constituencies, and five seats are allocated at the national level to parties that received at least 1% of the vote nationally, giving preference to those that did not win any of the 178 constituency seats.[10]
The 20 seats in the Central American Parliament are elected by proportional representation.
Presidential candidates[edit]
| Party | Presidential candidate | Vice presidential candidate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominican Liberation Party (PLD) | Gonzalo Castillo[11] | Margarita Cedeño | |
| Modern Revolutionary Party (PRM) | Luis Abinader[11] | Raquel Peña de Antuña | |
| Fuerza del Pueblo (FP) | Leonel Fernández | Sergia Elena de Séliman | |
| Alianza País (ALPAÍS) | Guillermo Moreno García[11] | Agustín González Morel | |
| National Citizen Will Party (PNVC) | Juan Cohen | Hugo McFarlane Kaluche | |
| Partido Demócrata Institucional (PDI) | Ismael Reyes Cruz | Frank Gene Troncoso Haché | |
Opinion polls[edit]
President[edit]
| Pollster | Date(s) | Castillo (PLD) | Abinader (PRM) | Fernandez (FP) | Moreno (ALPAIS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centro Económico del Cibao | 11–13 Oct 2019 | 29.7% | 43.7% | 23.6% | N/A |
| Centro Económico del Cibao | 3–5 Nov 2019 | 31% | 42.9% | 18.4% | 1.9% |
| Centro Economico del Cibao[12][13] | 29 Nov –1 Dec 2019 | 25.6% | 46.6% | 24.4% | N/A |
| Pool Logistic SRL | 1–5 Dec 2019 | 49% | 36% | 3.9% | N/A |
| Ideame | 3–10 Dec 2019 | 31.8% | 47.5% | 18.3% | N/A |
| ABC Marketing[permanent dead link] | 10–14 Dec 2019 | 22.6% | 47.3% | 20.9% | N/A |
| Sigma Dos | 15–17 Dec 2019 | 39.9% | 35% | 8% | N/A |
| Mark Penn/Stagwell[permanent dead link] | 8–10 Jan 2020 | 28% | 43% | 19% | N/A |
| Gallup-RD | 16–21 Jan 2020 | 31.4% | 42.2% | 15.5% | 1.2% |
| Gallup-Hoy | 16–21 Jan 2020 | 31.7% | 44.9% | 19.3% | N/A |
| CIES International | 31 Jan–2 Feb 2020 | 35% | 37% | 11% | 3% |
| Greenberg-Diario Libre | 21–24 Feb 2020 | 24% | 52% | 17% | 2% |
| CIES International | 23–25 Feb 2020 | 28.8% | 43.7% | 12.6% | 6.4% |
| CIMERAN< | 28–29 Feb 2020 | 25% | 52.5% | 17.5% | 3.5% |
| Centro Económico del Cibao | 28 Feb–5 Mar 2020 | 21.0% | 55.1% | 15.6% | N/A |
| Sigma Dos | 2–7 Apr 2020 | 38.8% | 36.6% | 9.6% | N/A |
| Horizon Research LLC | 7 Apr 2020 | 23.6% | 43.9% | 31.2% | N/A |
| Global Trend Research | 12–15 Apr 2020 | 22.9% | 43.1% | 30.4% | 0.8% |
| ASISA | 13–19 Apr 2020 | 20.4% | 44% | 29.1% | N/A |
| JB Consulting Group | 14–20 Apr 2020 | 46.6% | 31.1% | 3.6% | N/A |
| APD Consulting Group | 17–20 Apr 2020 | 24.1% | 54.4% | 11.8% | 4.6% |
| CIES International | 17–20 Apr 2020 | 33% | 39% | 9% | 4% |
| Centro Economico del Cibao | 18–19 Apr 2020 | 23.7% | 53.4% | 7.3% | 1% |
| Polimetrics | 22–25 Apr 2020 | 40.8% | 38.3% | 9.3% | 1.9% |
| CID Latinoamericana | 22–23 Apr 2020 | 40% | 38% | 8% | N/A |
| New Partners | 23–26 Apr 2020 | 27.4% | 52.1% | 9.9% | 2.1% |
| Market Reports | 25–27 Apr 2020 | 22.4% | 42.8% | 31.2% | N/A |
| Mercado & Cuantificaciones | 27–29 Apr 2020 | 30.3% | 52.3% | 12.3% | 1.7% |
| GIDL | 26 Apr–1 May 2020 | 23.2% | 41.9% | 32.4% | N/A |
| Datamarket | 1–3 May 2020 | 26% | 46% | 21% | 2% |
| Horizon Research LCC | 3–7 May 2020 | 22.8% | 41.3% | 33.5% | N/A |
| Effective Project Comunications[permanent dead link] | 4–7 May 2020 | 29% | 49% | 16% | 3% |
| Polimetric | 4–9 May 2020 | 40.4% | 37.7% | 8.8% | N/A |
| Centro Economico del Cibao | 11–12 May 2020 | 35.2% | 53.9% | 9.5% | N/A |
| ABC Marketing | 13–16 May 2020 | 26.5% | 55.6% | 14.5% | N/A |
| SISGLO | 17–20 May 2020 | 24.1% | 40.6% | 33.8% | N/A |
| Centro Economico del Cibao | 18–19 May 2020 | 34.6% | 53.3% | 9.9% | 2.2% |
| Elections & Proyect Corp | 20–22 May 2020 | 21.8% | 42.1% | 33.9% | N/A |
| IDEAME | 18–23 May 2020 | 31.5% | 51.8% | 14.3% | 1% |
| José Dorín Cabrera Mercadología | 21–23 May 2020 | 46.9% | 36.7% | 9.5% | 2.2% |
| Mark Penn/Stagwell | 20–25 May 2020 | 37% | 39% | 10% | N/A |
| APD Consulting Group | 21–25 May 2020 | 34.4% | 51.6% | 11.6% | 2.3% |
| CID Latinoamericana[14][15] | 23–24 May 2020 | 41% | 39% | 10% | 3% |
| ASISA | 13–19 Apr 2020 | 20.4% | 44% | 29.1% | N/A |
| Centro Economico del Cibao | 25–26 May 2020 | 34.0% | 53.5% | 10.3% | 2.1% |
| CIES International | 24–27 May 2020 | 29% | 52% | 10% | 6% |
| CYGNAL | 26 May–2 Jun 2020 | 28.2% | 54.6% | 13.9% | 3.4% |
| Mercado & Cuantificaciones | 28–30 May 2020 | 33% | 51.3% | 11.2% | 1.1% |
| Datamarket | 26–30 May 2020 | 27% | 44% | 21% | 2% |
| Polimetrics | 30–31 May 2020 | 40.7% | 37.5% | 8.5% | 2.6% |
| GIDL | 1–3 Jun 2020 | 21.5% | 40.7% | 33.4% | 1.7% |
| Mercado & Cuantificaciones | 2–5 Jun 2020 | 34.5% | 52.1% | 8.2% | N/A |
| New Partners | 2–5 Jun 2020 | 29.5% | 50.7% | 11.4% | N/A |
| Global Trend Research | 4–6 Jun 2020 | 25.7% | 40.3% | 30.8% | N/A |
| Gavindian Polsters | 4–8 Jun 2020 | 38% | 52% | 9% | 1% |
| Ideame | 5–9 Jun 2020 | 34.4% | 52.5% | 10.9% | 0.9% |
| Centro de Innovación y Políticas Públicas | 6–9 Jun 2020 | 36.3% | 52.3% | 7.7% | 1% |
| CID Latinoamericana | 9–11 Jun 2020 | 43% | 44% | 9% | 1% |
| Consulting and Field International | 9–12 Jun 2020 | 43% | 40% | 9% | 2% |
| Sigma Dos[16][17] | 12–14 Jun 2020 | 43.6% | 40.4% | 10.1% | 1.9% |
| John Zogby Strategies | 12–14 Jun 2020 | 34% | 54% | 9% | 2% |
| Datamarket | 12–14 Jun 2020 | 32% | 43% | 17% | 2% |
| Greenberg-Diario Libre | 11–16 Jun 2020 | 29% | 56% | 12% | 1% |
| Gallup | 12–16 Jun 2020 | 35.5% | 53.7% | 8.6% | 1.3% |
| Mercado y Cuantificaciones | 15–17 Jun 2020 | 33.5% | 55.8% | 7.0% | 0.3% |
| PoliRD | 16–18 Jun 2020 | 45.1% | 41.7% | 9.8% | 1.8% |
| ABC Marketing | 15–20 Jun 2020 | 32.6% | 54.8% | 10.4% | N/A |
| Market Reports | 18–21 Jun 2020 | 26.2% | 40.8% | 30.6% | N/A |
| Polismetrics | 20–25 Jun 2020 | 42.9% | 39.2% | 9.6% | 1.8% |
| Emevenca | 20–23 Jun 2020 | 41% | 46% | 8% | 2% |
| Mark Penn /Stagwell-SIN | 16–23 Jun 2020 | 35% | 47% | 11% | N/A |
| GIDL | 21–23 Jun 2020 | 23.8% | 43% | 29.7% | 1.2% |
| Centro Economico del Cibao | 22–23 Jun 2020 | 33.4% | 55.2% | 9.7% | 1.7% |
| NewPartners | 24–25 Jun 2020 | 29% | 54% | 10% | N/A |
Party identification and Congress[edit]
| Pollster | Date(s) | PLD | PRM | FP | PRSC | PRD | ALPAIS | N/A | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIES International | 19–22 Sep 2019 | 31% | 33% | N/A | 3.3% | 1.2% | 4.7% | 15.6% | 12.2% |
| Gallup-Hoy | 16–21 Jan 2020 | 37.5% | 43.3% | 8.5% | N/A | N/A | 0.1% | 7.6% | 2.9% |
| CIES International | 23–25 Feb 2020 | 27.5% | 43.6% | 10% | 3.8% | 1.3% | 2.5% | 11.3% | N/A |
| Makert Reports | 25–27 Apr 2020 | 29.1% | 34.7% | 19.1% | 3.6% | 2.3% | N/A | 6.8% | 4.2% |
| Datamarket[18] | 1–3 May 2020 | 27% | 37% | 7% | 6% | 4% | 2% | 6% | 11% |
| Effective Project Comunications[permanent dead link] | 4–7 May 2020 | 32% | 44% | 8% | 6% | 4% | 1% | 2% | 3% |
| José Dorín Cabrera Mercadología | 21–23 May 2020 | 34.2% | 23.2% | 8.4% | N/A | N/A | 0.5% | 30.1% | 3.6% |
| CID Latinoamericana | 23–24 May 2020 | 45% | 38% | 6% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Datamarket | 26–30 May 2020 | 27% | 37% | 7% | 6% | 4% | 2% | 6% | 11% |
| CYGNAL | 26 May–2 Jun 2020 | 26.7% | 40.5% | 9.5% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Polimetrics | 30–31 May 2020 | 35.4% | 29.9% | 8.9% | 0.9% | N/A | N/A | 25.7% | 9.2% |
| CID Latinoamerica[permanent dead link] | 9–11 Jun 2020 | 43% | 40% | 7% | 1% | 2% | 1% | 5% | 1% |
| Mercados y Cuantificaciones | 15–17 Jun 2020 | 34% | 47.8% | 5.3% | 1.1% | 1.1% | 0.4% | 9.3% | 1% |
| ABC Marketing | 15–20 Jun 2020 | 29.8% | 46.7% | 12.3% | 3.1% | 6.0% | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Market Reports | 18–21 Jun 2020 | 27.3% | 33.2% | 22.2% | 3.6% | 2.3% | N/A | 6.8% | 4.6% |
| GIDL | 21–23 Jun 2020 | 23.7% | 34.7% | 21.7% | 4.2% | 1.3% | N/A | 8.2% | N/A |
| NewPartners | 24–25 Jun 2020 | 28% | 50% | 6% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 13% | 1% |
Conduct[edit]
It was initially reported that representatives of the Organization of American States (OAS) would arrive to the Dominican Republic on 13 February 2020 to monitor the elections.[19][20][21] The general election to elect the President and members of the Dominican Republic parliament, which was postponed from the scheduled May 17, 2020 date due to the COVID-19 pandemic, was later held on July 5, 2020.[22][23]
Local media reported that the elections proceeded smoothly, except for one incident, when a person was shot inside a polling station after an argument erupted between rival party supporters.[24]
Results[edit]
President[edit]
Luis Abinader won the presidential election in the first round, obtaining over 50% of the vote. During the election count, the ruling Dominican Liberation Party's candidate Gonzalo Castillo conceded defeat, stating that the official count "shows that there is an irreversible trend and that from now on we have a president-elect... Our congratulations to Mr Luis Abinader."[7] Former President Leonel Fernández, who left the ruling party and ran for the presidency as a member of the People's Force party, also conceded defeat.[7] Abinader was sworn in as President of the Dominican Republic on August 16, 2020.[8]
| Candidates | Party | Votes | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luis Abinader | Modern Revolutionary Party[a] | 2,154,866 | 52.51 |
| Gonzalo Castillo | Dominican Liberation Party[b] | 1,537,078 | 37.46 |
| Leonel Fernández | People's Force[c] | 365,226 | 8.90 |
| Guillermo Moreno García | Country Alliance | 39,458 | 0.96 |
| Ismael Reyes Cruz | Institutional Democratic Party | 3,484 | 0.09 |
| Juan Cohen | National Citizen Will Party | 3,250 | 0.08 |
| Invalid/blank votes | 59,943 | – | |
| Total | 4,163,305 | 100 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 7,529,932 | 55.29 | |
| Source: JCE | |||
Senate[edit]
The Modern Revolutionary Party won an absolute majority in the Senate on their own, seeing their seat total increase by 15, while the ruling Dominican Liberation party lost over 75% of their prior seats.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modern Revolutionary Party | 1,768,588 | 45.24 | 17 | +15 | ||||
| Dominican Liberation Party | 1,267,168 | 32.41 | 6 | –20 | ||||
| People's Force | 141,836 | 3.63 | 1 | New | ||||
| Social Christian Reformist Party | 116,353 | 2.98 | 6 | +5 | ||||
| Dominican Revolutionary Party | 111,476 | 2.85 | 0 | –1 | ||||
| National Unity Party | 55,057 | 1.41 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Country Alliance | 54,209 | 1.39 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Dominicans for Change | 48,365 | 1.24 | 1 | +1 | ||||
| Social Democratic Institutional Bloc | 48,124 | 1.23 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Civic Renovation Party | 36,030 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Alternative Democratic Movement | 27,745 | 0.71 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Liberal Reformist Party | 25,276 | 0.65 | 0 | –1 | ||||
| Broad Front | 24,863 | 0.64 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Revolutionary Social Democratic Party | 23,093 | 0.59 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Alliance for Democracy | 20,868 | 0.53 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Christian People's Party | 18,817 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Quisqueyano Christian Democratic Party | 17,125 | 0.44 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Dominican Humanist Party | 15,963 | 0.41 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Liberal Party of Action | 14,537 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| National Progressive Force | 14,485 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Christian Democratic Union | 12,392 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Possible Country | 11,136 | 0.28 | 0 | New | ||||
| Independent Revolutionary Party | 9,628 | 0.25 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| People's Democratic Party | 9,568 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Institutional Democratic Party | 8,971 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| National Citizen Will Party | 7,651 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 120,562 | – | – | – | ||||
| Total | 4,029,886 | 100 | 32 | 0 | ||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 6,934,053 | 58.12 | – | – | ||||
| Source: JCE | ||||||||
Chamber of Deputies[edit]
The Modern Revolutionary Party won a plurality of votes and seats, seeing their seat count more than double. The ruling Dominican Liberation Party lost nearly 30% of their prior seats. No party has a majority on their own in the Chamber, meaning alliances or coalitions will need to be made to guarantee the passage of bills. A total of 96 seats is needed for a majority.
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modern Revolutionary Party | 1,634,860 | 40.84 | 86 | +44 | ||||
| Dominican Liberation Party | 1,261,802 | 31.52 | 75 | –31 | ||||
| Dominican Revolutionary Party | 220,939 | 5.52 | 4 | –12 | ||||
| People's Force | 170,993 | 4.27 | 3 | New | ||||
| Social Christian Reformist Party | 165,800 | 4.14 | 6 | –12 | ||||
| Country Alliance | 71,899 | 1.80 | 2 | +1 | ||||
| Dominicans for Change | 45,162 | 1.13 | 2 | +2 | ||||
| Dominican Humanist Party | 42,597 | 1.06 | 1 | +1 | ||||
| Civic Renovation Party | 39,589 | 0.99 | 1 | +1 | ||||
| Social Democratic Institutional Bloc | 37,235 | 0.93 | 2 | +2 | ||||
| Revolutionary Social Democratic Party | 33,362 | 0.83 | 1 | +1 | ||||
| Alternative Democratic Movement | 32,723 | 0.82 | 0 | –1 | ||||
| Broad Front | 30,429 | 0.76 | 3 | +2 | ||||
| National Unity Party | 27,600 | 0.69 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Alliance for Democracy | 26,570 | 0.66 | 2 | +2 | ||||
| Christian People's Party | 20,894 | 0.52 | 0 | –1 | ||||
| Quisqueyano Christian Democratic Party | 19,414 | 0.49 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| Christian Democratic Union | 18,199 | 0.46 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Liberal Party of Action | 17,655 | 0.44 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Liberal Reformist Party | 15,652 | 0.39 | 1 | –2 | ||||
| Possible Country | 15,346 | 0.38 | 0 | New | ||||
| National Citizen Will Party | 12,517 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Independent Revolutionary Party | 12,368 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| National Progressive Force | 10,959 | 0.27 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| People's Democratic Party | 10,598 | 0.27 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Institutional Democratic Party | 7,997 | 0.20 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 151,946 | – | – | – | ||||
| Total | 4,003,159 | 100 | 190 | 0 | ||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 7,529,932 | 55.18 | – | – | ||||
| Source: JCE, JCE | ||||||||
Notes[edit]
- ^ In alliance with the Revolutionary Social Democratic Party, Dominican Humanist Party, Alliance for Democracy, País Posible, Broad Front, and the Dominicans for Change Party
- ^ In alliance with the Alternative Democratic Movement, Christian Democratic Union Party, Civic Renovation Party, Popular Democratic Party, Independent Revolutionary Party, and Dominican Revolutionary Party
- ^ In alliance with the Social Christian Reformist Party, Institutional Socialist Democratic Bloc, National Unity Party, National Progressive Force, and Quisqueyano Christian Democratic Party
References[edit]
- ^ "Padrón para las elecciones de mayo tendrá un incremento de más de 69 mil electores" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 14 January 2020. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- ^ "La JCE pospone las elecciones presidenciales y congresuales para el 5 de julio" (in Spanish). Diario Libre. 14 April 2020. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- ^ "Elecciones de 2020 son un reto para la JCE" (in Spanish). El Día. 2 August 2017. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
- ^ "Este será el orden de los partidos en la próxima boleta electoral" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 10 December 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
- ^ "Candidatos presidenciales podrán gastar más de 900 millones durante campaña electoral" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ "La JCE aprueba tres formatos distintos para boletas de mayo" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 19 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d BBC News (6 July 2020). "Change in Dominican Republic as opposition wins presidency". Yahoo News. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ a b Associated Press (16 August 2020). "Luis Abinader Sworn in as Dominican Leader; Pompeo Attends". U.S. News. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ Senado (Senate) IPU
- ^ Cámara de Diputados (Chamber of Deputies) IPU
- ^ a b c "Once partidos gestan coalición para desplazar al PLD del poder" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- ^ "Luis derrotaría fácil a Gonzalo y a Leonel en primera vuelta, según encuesta". Acento (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 June 2020.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Diario, Listin (10 December 2019). "Encuesta otorga mayoría de simpatías a Luis Abinader". listindiario.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ "Resumen y Predicciones de Encuestas Elecciones 2020 Republica Dominicana". ElInfluyente.com. 16 June 2020. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ Hoy (1 June 2020). "Encuesta dice ya Gonzalo Castillo está arriba de Luis Abinader en primera y segunda vuelta | Hoy Digital" (in Spanish). Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ Diario, Listin (21 June 2020). "Encuesta da a Gonzalo 43.6%, Abinader 40.4% y Leonel 10.1%". listindiario.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ Noticias, R. C. (21 June 2020). "Gonzalo Castillo ganaría las elecciones con una ventaja de más de 3 puntos frente a Luis Abinader, según encuesta". Roberto Cavada (in Spanish). Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- ^ Noticias, R. C. (5 May 2020). "Abinader ganaría elecciones con 46 %; Gonzalo Castillo 26 % y Leonel Fernández 21 %, según encuesta Datamarket". Roberto Cavada (in Spanish). Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ "Misión de OEA observará elecciones del 2020 en República Dominicana" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 25 November 2019. Retrieved 25 November 2019.
- ^ "Observadores electorales de la OEA harán visita preliminar la próxima semana" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 17 January 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2020.
- ^ "JCE recibirá observadores de 20 países para elecciones municipales" (in Spanish). Listin Diario. 9 February 2020. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ^ "Dominicans vote in election postponed over virus". 5 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020 – via www.bbc.com.
- ^ "Polls open in Dominican Republic presidential election". France 24. 5 July 2020. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- ^ https://news.yahoo.com/dominican-republic-votes-election-postponed-004941501.html


