Este artículo se basa demasiado en referencias a fuentes primarias . ( Octubre de 2011 ) ( Obtenga información sobre cómo y cuándo eliminar este mensaje de plantilla ) |
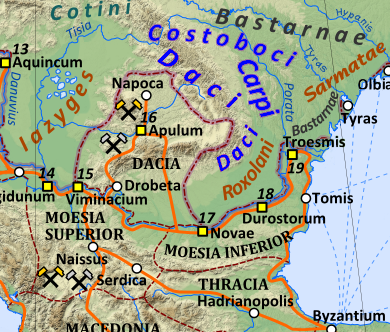
Los Bastarnae ( variantes latinas : Bastarni o Basternae ; griego antiguo : Βαστάρναι o Βαστέρναι ) fueron un pueblo antiguo que entre el 200 a. C. y el 300 d. C. habitó la región entre los Cárpatos y el río Dnieper , al norte y al este de la antigua Dacia . Los Peucini , descritos como una rama de los Bastarnae por escritores grecorromanos, ocuparon la región al norte del Delta del Danubio .
La afiliación etnolingüística de los Bastarnae fue probablemente celta , que es apoyada por los primeros historiadores. [1] [2] Sin embargo, fuentes históricas posteriores implican un origen germánico o escito-sármata . [3] [4] [5] [6] A menudo se les asocia con los alemanes, o los pueblos "entre los celtas y los alemanes". [7] [8] El escenario más probable es que originalmente eran una tribu celta, originalmente residente en la parte baja del río Vístula.Valle. Alrededor del 200 a. C., estas tribus emigraron, posiblemente acompañadas de algunos elementos germánicos, hacia el sureste hacia la región del Ponto Norte. Algunos elementos parecen haber sido asimilados, hasta cierto punto, por los sármatas circundantes en el siglo III.
Aunque en gran parte sedentarios, algunos elementos pueden haber adoptado un estilo de vida seminómada. Hasta ahora, ningún sitio arqueológico se ha atribuido de manera concluyente a los Bastarnae. Los horizontes arqueológicos más frecuentemente asociados por los estudiosos con los Bastarnae son las culturas Zarubintsy y Poienesti-Lukashevka .
Los bastarnos entraron en conflicto por primera vez con los romanos durante el siglo I a.C. cuando, en alianza con los dacios y sármatas, resistieron sin éxito la expansión romana en Moesia y Panonia . Más tarde, parece que mantuvieron relaciones amistosas con el Imperio Romano durante los dos primeros siglos d.C. Esto cambió c. 180, cuando los Bastarnae se registran como participantes en una invasión del territorio romano, una vez más en alianza con elementos sármatas y dacios. A mediados del siglo III, los Bastarnae formaban parte de una gran coalición de tribus del bajo Danubio liderada por el gótico que invadió repetidamente las provincias balcánicas del Imperio Romano.
Muchos bastarnos fueron reasentados dentro del Imperio Romano a finales del siglo III.
Fuentes antiguas [ editar ]
Según Polibio (200-118 a. C.):
"Llegó una misión de los dardanianos, que hablaba de los bastarnos, su número, el enorme tamaño y el valor de sus guerreros, y también señalaba que Perseo y los gálatas estaban aliados con esta tribu. Dijeron que tenían mucho más miedo. de él que de los Bastarnae, y suplicaron ayuda ". [9]
Según Livio (64 a. C. - 17 d. C.):
"El camino al Hadriático y a Italia pasaba por el Scordisci; esa era la única ruta practicable para un ejército, y se esperaba que los Scordisci concedieran un paso a los Bastarnae sin ninguna dificultad, porque ni en habla ni en hábitos eran diferentes, y se esperaba que unieran fuerzas con ellos cuando vieran que iban a conseguir el saqueo de una nación muy rica ". [2]
Según Estrabón (64 a. C. - 24 d. C.):
"Sin embargo, se desprende del" climata "y de las distancias paralelas que si uno viaja longitudinalmente hacia el este, se encuentra con las regiones que están alrededor de Borysthenes y que están al norte del Ponto; pero lo que está más allá de Alemania y lo que más allá de los países que siguen a Alemania, ya sea que se diga que los Bastarnae, como sospechan la mayoría de los escritores, o que otros se encuentran en el medio, ya sea los Iazyges o los Roxolani, o algunos otros habitantes de los carromatos, no es fácil decir; ni aún si se extienden hasta el océano en toda su longitud, o si alguna parte es inhabitable por razón del frío u otra causa, o si incluso una raza diferente de personas, sucediendo a los alemanes, se encuentra entre los mar y los alemanes orientales.Y esta misma ignorancia prevalece también con respecto al resto de los pueblos que vienen luego en orden por el norte; porque no sé ni los Bastarnae, ni los Sauromatae, ni, en una palabra, ninguno de los pueblos que habitan sobre el Ponto, ni qué tan lejos están del Mar Atlántico, ni si sus países limitan con él ".[3]
Según Plutarco (46-120 d.C.):
También incitó en secreto a los galos asentados a lo largo del Danubio, que se llaman Basternae, una hueste ecuestre y guerrera; e invitó a los ilirios, a través de Genthius, su rey, a participar con él en la guerra. Y prevaleció un informe de que el Los bárbaros habían sido contratados por él para atravesar la Baja Galia, a lo largo de la costa del Adriático, y hacer una incursión en Italia ". [1]
Según Tácito (56-120 d.C.):
"En cuanto a las tribus de los Peucini, Veneti y Fenni, tengo dudas sobre si debería clasificarlas entre los alemanes o los Sarmatæ, aunque de hecho los Peucini llamados por algunos Bastarnæ, son como los alemanes en su idioma, modo de vida y en la permanencia de sus asentamientos. Todos viven en la inmundicia y la pereza, y debido a los matrimonios mixtos de los jefes se están degradando en cierto grado en semejanza a los Sarmatæ ". [4]
Según Cassius Dio (155-235 d.C.):
"Durante el mismo período en el que ocurrieron estos hechos, Marco Craso fue enviado a Macedonia y Grecia y llevado a la guerra con los dacios y los bastarnos. Ya he dicho quiénes eran los primeros y por qué se habían vuelto hostiles; los bastarnos, por otro lado. , quienes están debidamente clasificados como escitas, habían cruzado en ese momento el Ister y sometido la parte de Moesia frente a ellos, y luego sometido a los triballi que colindan con este distrito ya los dardani que habitan el país tribaliano ".
Según Zosismus ( 490s -510 DC):
"También dejó en Tracia a los Bastarnae, un pueblo escita, que se sometieron a él, dándoles tierras para habitar allí, por lo que observaron las leyes y costumbres romanas". [6]
Etimología [ editar ]
El origen del nombre tribal es incierto. Ni siquiera está claro si era un exónimo (un nombre que les atribuían los forasteros) o un endónimo (un nombre con el que los Bastarnae se describían a sí mismos). Una cuestión relacionada es si los grupos denominados "Bastarnae" por los romanos se consideraban a sí mismos un grupo étnico distinto en absoluto (endónimo) o si era un exónimo genérico utilizado por los grecorromanos para denotar un grupo dispar de tribus de la región de los Cárpatos que no podría clasificarse como dacios o sármatas.
Una posible derivación es de la palabra protogermánica * bastjan (de la raíz protoindoeuropea * bʰas- ), que significa "atar" o "atar". [10] En este caso, Bastarnos puede haber tenido el significado original de una coalición o Bund de tribus.
Es posible que el término romano basterna , que denota un tipo de carreta o litera, se derive del nombre de este pueblo (o, si es un exónimo, que de él se derive el nombre del pueblo) que eran conocidos, como muchas tribus germánicas, para viajar en un tren de carromatos para sus familias. [11] [ verificación fallida - ver discusión ]
También se ha sugerido que el nombre está vinculado con la palabra germánica bastardo , que significa ilegítimo o mestizo, pero Roger Batty considera que esta derivación es poco probable. [12] Si el nombre es un endónimo, entonces esta derivación es poco probable, ya que la mayoría de los endónimos tienen significados halagadores (por ejemplo, "valiente", "fuerte", "noble").
Trubačev [13] propone una derivación de persa antiguo , Avestan bast- "unido, atado; esclavo" (cf. Ossetic bættən "bind", estopa "unido") y iraní * arna- "descendencia", equiparándolo con el δουλόσποροι " esclavo Sporoi "mencionado por Nonnus y Cosmas , donde los Sporoi son las personas que Procopio menciona como los antepasados de los eslavos . [14]
Territorio [ editar ]
La patria original de los Bastarnae sigue siendo incierta. Los niños y de Shchukin argumentan a favor de un origen en el este de Pomerania en el Báltico costa del actual noroeste de Polonia , por motivos de correspondencias en el material arqueológico, por ejemplo, un estilo de Pomerania peroné encuentra en un sitio Poieneşti en Moldavia , [15] aunque Batty considera que la evidencia es insuficiente. [16] Babeş identifica al Sidoni, una rama del Bastarnae que Estrabón coloca al norte del delta del Danubio [17] con el Sidini ubicado por Ptolomeo en Pomerania. [18]
Batty sostiene que las fuentes grecorromanas del siglo I d.C. ubican la tierra natal de Bastarnae en el lado norte de la cordillera de los Cárpatos del Norte , abarcando el sureste de Polonia y el suroeste de Ucrania (es decir, la región tradicionalmente conocida como Galicia ). [19] Plinio ubica a los Bastarnae entre los suevos [20] y los dacios ( contermini Dacis ). [21] El mapa de Peutinger (producido ca. 400 d. C., pero que incluye material de tan temprano como el siglo I) muestra a los Bastarnae (mal escrito Blastarni) al norte de los Cárpatos y parece nombrar a los Cárpatos gallegos como Alpes Bastarnicae . [19]
Desde Galicia, los Bastarnae se expandieron a las regiones de Moldavia y Besarabia , llegando al delta del Danubio . Strabo describe a los Bastarnae como habitantes del territorio "entre el Ister (el Danubio ) y el Borysthenes (el Dnieper )". Identifica tres sub-tribus de los bastarnos: la Atmoni , Sidoni y Peucini . Estos últimos derivaron su nombre de Peuce , una gran isla en el delta del Danubio que habían colonizado. [17] El geógrafo Ptolomeo del siglo II afirma que el Carpianio Carpi (que se cree que ocupó Moldavia) separó a los Peucini de los otros Bastarnae "por encima de Dacia " (es decir, al norte de Dacia). [22]
Por tanto, parece que los Bastarnae se asentaron en un vasto arco que se extiende alrededor de los flancos norte y este de los Cárpatos desde el sureste de Polonia hasta el delta del Danubio. El grupo más grande habitaba las laderas norte y este de los Cárpatos y la región entre los ríos Prut y Dnieper (actual Moldavia / Ucrania occidental), mientras que un grupo separado (Peucini, Sidoni y Atmoni) habitaba en el Danubio y al norte. Región delta. [23]
Afiliación etnolingüística [ editar ]
Scholars hold divergent theories about the ethnicity of the Bastarnae. One view, following what appears to be the most authoritative view among earliest scholars, is that they spoke a Celtic language.[2] However others hold that they were Scythian/Germanic,[3] or mixed Germanic/Sarmatian.[4] A fringe theory is that they were Proto-Slavic.[13] Shchukin argues that the ethnicity of the Bastarnae was unique and rather than trying to label them as Celtic, Germanic or Sarmatian, it should be accepted that the "Basternae were the Basternae".[24] Batty argues that assigning an "ethnicity" to the Bastarnae is meaningless; as in the context of the Iron Age Pontic-Danubian region, with its multiple overlapping peoples and languages, ethnicity was a very fluid concept: it could and did change rapidly and frequently, according to socio-political vicissitudes. This was especially true of the Bastarnae, who are attested over a relatively vast area.[25]
Celtic[edit]
A leading reason to consider the Bastarnae as Celtic is that the regions they are documented to have occupied (the northern and eastern slopes of the Carpathians) overlapped to a great extent with the locations of Celtic tribes attested in the northern Carpathians. (The modern name of this region, Galicia, is generally regarded as having a later origin, in either a Slavic or Turkic language. However, some scholars have instead suggested that the name Galicia may derive from its former Celtic inhabitants the Taurisci, Osi, Cotini and Anartes of Slovakia and northern Romania and the Britogalli of the Danube Delta region.[26]) In addition, archaeological cultures which some scholars have linked to the Bastarnae (Poieneşti-Lukashevka and Zarubintsy) display pronounced Celtic affinities. Finally, the arrival of the Bastarnae in the Pontic-Danubian region, which can be dated to 233–216 BC according to two ancient sources,[27] coincides with the latter phase of Celtic migration into the region (400–200 BC).
The earliest historians give a Celtic or Gallic origin to the Bastarnae. Roman historian Livy, writing in c. 10 AD, attests that the Bastarnae spoke Celtic. Relating the Bastarnic invasion of the Balkans of 179 BC (see Allies of Philip of Macedon below), he describes them then as "they were not very different in either language or manners" to the Celtic tribe of the Scordisci, a tribe of Pannonia. The Scordisci are described as Celtic by Strabo (although he adds that they had mingled with Illyrians and Thracians).[28] The Greek historian Plutarch inform us that the Roman consul Hostilius "secretly stirred up the Gauls settled along the Danube, who are called Basternae".[1]
However, a Celtic identity for the Bastarnae is apparently contradicted by Polybius (writing ca. 150 BC), who was an actual contemporary of the events described, unlike Livy, who was writing some 200 years later. Polybius clearly distinguishes the Bastarnae from the "Galatae" (i.e. Celts): "An embassy from the Dardani arrived [at the Roman Senate], talking of the Bastarnae, their huge numbers, the strength and valour of their warriors, and also reporting that Perseus [king of Macedon] and the Galatae were in league with this tribe."[29] In addition, inscription AE (1905) 14, recording a campaign on the Hungarian Plain by the Augustan-era general Marcus Vinucius (10 BC[30] or 8 BC[31]), also appears to distinguish the Bastarnae from neighbouring Celtic tribes: "Marcus Vinucius... governor of Illyricum, the first [Roman general] to advance across the river Danube, defeated in battle and routed an army of Dacians and Basternae, and subjugated the Cotini, Osi,...[missing tribal name] and Anartii to the power of the emperor Augustus and of the people of Rome."[32]
The three names of Bastarnae leaders found in ancient sources are of Celtic origin: Cotto,[33] Clondicus[34] and Teutagonus.[35][36]
Germanic[edit]
Greco-Roman geographers of the 1st century AD are unanimous and specific that the Bastarnae were Germanic in language and culture. The Greek geographer Strabo (writing c. 5–20 AD) says the Bastarnae are "of Germanic stock".[17] The Roman geographer Pliny the Elder (c. 77 AD), classifies the Bastarnae and Peucini as being one of the five main subdivisions of Germanic peoples, the other subdivisions being three West Germanic groups, the Inguaeones, Istuaeones and Hermiones, and the East Germanic Vandili.[37]
The Roman historian Tacitus (c. 100 AD) describes the Bastarnae as Germans with substantial Sarmatian influence, but moves on to state: "The Peucini, however, who are sometimes called Bastarnae, are like the Germans in their language, way of life and types of dwelling."[38]
Scytho-Sarmatian[edit]
Strabo includes the Roxolani, generally considered by scholars to have been a Sarmatian tribe, in a list of Bastarnae subgroups.[17] However, this may simply be an error due to the close proximity of the two peoples north of the Danube Delta. In the 3rd century, the Greek historian Dio Cassius states that the "Bastarnae are properly classed as Scythians" and "members of the Scythian race".[39] Likewise, the 6th-century historian Zosimus, reporting events around 280 AD, refers to "the Bastarnae, a Scythian people".[40] However, it appears that these late Greco-Roman chroniclers used the term "Scythian" more often in a geographical sense (for inhabitants of the region they called Scythia, i.e. the Pontic region north of the Danube) rather than in an ethnic one (for members of the Scythian people, steppe nomads of Iranic origin, related to the Sarmatians, who had supplanted the Scythians' dominance of the steppes in the period BC). For example, Zosimus also routinely refers to the Goths, who were undoubtedly Germanic-speakers, as "Scythians".
It is possible that some Bastarnae may have been assimilated by the surrounding (and possibly dominant) Sarmatians, perhaps adopting their tongue (which belonged to the Iranian group of Indo-European languages) and customs. Thus Tacitus' comment that "mixed marriages are giving [the Bastarnae] to some extent the vile appearance of the Sarmatians".[38] On the other hand, the Bastarnae maintained a separate name until ca. 300 AD, probably implying retention of their distinctive ethno-linguistic heritage up to that time.[41] It seems likely, on balance, that the core population of Bastarnae had always been, and continued to be, Germanic in language and culture.
Material culture[edit]
According to Malcolm Todd, traditional archaeology has not been able to construct a typology of Bastarnae material culture, and thus to ascribe particular archaeological sites to the Bastarnae.[42] A complicating factor is that the regions where Bastarnae are attested contained a patchwork of peoples and cultures (Sarmatians, Scythians, Dacians, Thracians, Celts, Germans and others), some sedentary, some nomadic. In any event, post-1960s archaeological theory has questioned the validity of equating material "cultures", as defined by archaeologists, with distinct ethnic groups. In this view, it is impossible to attribute a "culture" to a particular ethnic group: it is likely that the material cultures discerned in the region belonged to several, if not all, of the groups inhabiting it. These cultures probably represent relatively large-scale socio-economic interactions between disparate communities of the broad region, possibly including mutually antagonistic groups.[42]
It is not even certain whether the Bastarnae were sedentary, nomadic or semi-nomadic. Tacitus' statement that they were "German in their way of life and types of dwelling" implies a sedentary bias, but their close relations with the Sarmatians, who were nomadic, may indicate a more nomadic lifestyle for some Bastarnae, as does their attested wide geographical range.[43] If the Bastarnae were nomadic, then the sedentary "cultures" identified by archaeologists in their lebensraum would not represent them. Nomadic peoples generally leave scant traces, due to the impermanent materials and foundations used in the construction of their dwellings.
Scholars have identified two closely related sedentary "cultures" as possible candidates to represent the Bastarnae (among other peoples) as their locations broadly correspond to where ancient sources placed the Basternae: the Zarubintsy culture lying in the forest-steppe zone in northern Ukraine and southern Belarus, and the Poieneşti-Lukashevka culture (Lucăşeuca) in northern Moldavia.[27][44] These cultures were characterised by agriculture, documented by numerous finds of sickles. Dwellings were either of surface or semi-subterranean types, with posts supporting the walls, a hearth in the middle and large conical pits located nearby. Some sites were defended by ditches and banks, structures thought to have been built to defend against nomadic tribes from the steppe.[45] Inhabitants practiced cremation. Cremated remains were either placed in large, hand-made ceramic urns, or were placed in a large pit and surrounded by food and ornaments such as spiral bracelets and Middle to Late La Tène-type fibulae (attesting the continuing strength of Celtic influence in this region).
A major problem with associating the Poieneşti-Lukashevka and Zarubintsy cultures with the Bastarnae is that both cultures had disappeared by the early 1st century AD, while the Bastarnae continue to be attested in those regions throughout the Roman Principate.[46] Another issue is that the Poieneşti-Lukashevka culture has also been attributed to the Costoboci, a people considered ethnically Dacian by mainstream scholarship, who inhabited northern Moldavia, according to Ptolemy (ca. 140 AD). Indeed, Mircea Babeş and Silvia Theodor, the two Romanian archaeologists who identified Lukashevka as Bastarnic, nevertheless insisted that the majority of the population in the Lukashevka sphere (in northern Moldavia) was "Geto-Dacian".[19] A further problem is that neither of these cultures were present in the Danube Delta region, where a major concentration of Bastarnae are attested by the ancient sources.[27]
Starting in about 200 AD, the Chernyakhov culture became established in the modern-day western Ukraine and Moldova region inhabited by the Bastarnae. The culture is characterised by a high degree of sophistication in the production of metal and ceramic artefacts, as well as of uniformity over a vast area. Although this culture has conventionally been identified with the migration of the Gothic ethnos into the region from the northwest, Todd argues that its most important origin is Scytho-Sarmatian. Although the Goths certainly contributed to it, so probably did other peoples of the region such as the Dacians, proto-Slavs, Carpi and possibly the Bastarnae.[47]
Relations with Rome[edit]
Roman Republican era (to 30 BC)[edit]
Allies of Philip of Macedon (179–8 BC)[edit]
The Bastarnae first appear in the historical record in 179 BC, when they crossed the Danube in a massive force. They did so at the invitation of their long-time ally, King Philip V of Macedon, a direct descendant of Antigonus, one of the Diadochi, the generals of Alexander the Great who had shared his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Macedonian king had suffered a disastrous defeat at the hands of the Romans in the Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC), which had reduced him from a powerful Hellenistic monarch to the status of a petty client-king with a much-reduced territory and a tiny army.[Note 1] After nearly 20 years of slavish adherence to the Roman Senate's dictats, Philip had been goaded by the incessant and devastating raiding of the Dardani, a warlike Thraco-Illyrian[49] tribe on his northern border, which his treaty-limited army was too small to counter effectively. Counting on the Bastarnae, with whom he had forged friendly relations, he plotted a strategy to deal with the Dardani and then to regain his lost territories in Greece and his political independence. First, he would unleash the Bastarnae against the Dardani. After the latter had been crushed, Philip planned to settle Bastarnae families in Dardania (southern Kosovo/Skopje region) to ensure that the region was permanently subdued. In a second phase, Philip aimed to launch the Bastarnae on an invasion of Italy via the Adriatic coast. Although he was aware that the Bastarnae were likely to be defeated, Philip hoped that the Romans would be distracted long enough to allow him to reoccupy his former possessions in Greece.[33]
However, Philip, now 60 years of age, died before the Bastarnae could arrive. The Bastarnae host was still en route through Thrace, where it became embroiled in hostilities with the locals, who had not provided them with sufficient food at affordable prices as they marched through. Probably in the vicinity of Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv, Bulgaria), the Bastarnae broke out of their marching columns and pillaged the land far and wide. The terrified local Thracians took refuge with their families and animal herds on the slopes of Mons Donuca (Mount Musala), the highest mountain in Thrace. A large force of Bastarnae chased them up the mountain, but were driven back and scattered by a massive hailstorm. Then the Thracians ambushed them, turning their descent into a panic-stricken rout. Back at their wagon fort in the plain, around half of the demoralised Bastarnae decided to return home, leaving c. 30,000 to press on to Macedonia.[34]
Philip's son and successor Perseus, while protesting his loyalty to Rome, deployed his Bastarnae guests in winter quarters in a valley in Dardania, presumably as a prelude to a campaign against the Dardani the following summer. However, in the depths of winter their camp was attacked by the Dardani. The Bastarnae easily beat off the attackers, chased them back to their chief town and besieged them, but they were surprised in the rear by a second force of Dardani, which had approached their camp stealthily by mountain paths, and proceeded to storm and ransack it. Having lost their entire baggage and supplies, the Bastarnae were obliged to withdraw from Dardania and to return home. Most perished as they crossed the frozen Danube on foot, only for the ice to give way.[50] Despite the failure of Philip's Bastarnae strategy, the suspicion aroused by these events in the Roman Senate, which had been warned by the Dardani of the Bastarnae invasion, ensured the demise of Macedonia as an independent state.[51] Rome declared war on Perseus in 171 BC and after the Macedonian army was crushed at the Battle of Pydna (168 BC), Macedonia was split up into four Roman puppet-cantons (167 BC).[52] Twenty-one years later, these were in turn abolished and annexed to the Roman Republic as the province of Macedonia (146 BC).
Allies of Getan high king Burebista (62 BC)[edit]
The Bastarnae first came into direct conflict with Rome as a result of expansion into the lower Danube region by the proconsuls (governors) of Macedonia in 75–72 BC. Gaius Scribonius Curio (proconsul 75–73 BC) campaigned successfully against the Dardani and the Moesi, becoming the first Roman general to reach the Danube with his army.[53] His successor, Marcus Licinius Lucullus (brother of the famous Lucius Lucullus), campaigned against the Thracian Bessi tribe and the Moesi, ravaging the whole of Moesia, the region between the Haemus (Balkan) mountain range and the Danube. In 72 BC, his troops occupied the Greek coastal cities of Scythia Minor (modern Dobruja region, Romania/Bulgaria),[Note 2] which had sided with Rome's Hellenistic arch-enemy, King Mithridates VI of Pontus, in the Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC).[55]
The presence of Roman forces in the Danube Delta was seen as a major threat by all the neighbouring transdanubian peoples: the Peucini Bastarnae, the Sarmatians and, most importantly, by Burebista (ruled 82–44 BC), king of the Getae. The Getae occupied the region today called Wallachia as well as Scythia Minor and were either a Dacian- or Thracian- speaking people.[Note 3] Burebista had unified the Getae tribes into a single kingdom, for which the Greek cities were vital trade outlets. In addition, he had established his hegemony over neighbouring Sarmatian and Bastarnae tribes. At its peak, the Getae kingdom reportedly was able to muster 200,000 warriors. Burebista led his transdanubian coalition in a struggle against Roman encroachment, conducting many raids against Roman allies in Moesia and Thrace, penetrating as far as Macedonia and Illyria.[60]
The coalition's main chance came in 62 BC, when the Greek cities rebelled against Roman rule. In 61 BC, the notoriously oppressive and militarily incompetent proconsul of Macedonia, Gaius Antonius, nicknamed Hybrida ("The Monster"), an uncle of the famous Mark Antony, led an army against the Greek cities. As his army approached Histria, Antonius detached his entire mounted force from the marching column and led it away on a lengthy excursion, leaving his infantry without cavalry cover, a tactic he had already used with disastrous results against the Dardani.[61] Dio implies that he did so out of cowardice, in order to avoid the imminent clash with the opposition, but it is more likely that he was pursuing a large enemy cavalry force, probably Sarmatians. A Bastarnae host, which had crossed the Danube to assist the Histrians, promptly attacked, surrounded and massacred the Roman infantry, capturing several of their vexilla (military standards).[62] This battle resulted in the collapse of the Roman position on the lower Danube. Burebista apparently annexed the Greek cities (55–48 BC).[63] At the same time, the subjugated "allied" tribes of Moesia and Thrace evidently repudiated their treaties with Rome, as they had to be reconquered by Augustus in 29–8 BC (see below).
In 44 BC, Roman dictator-for-life Julius Caesar planned to lead a major campaign to crush Burebista and his allies once and for all, but he was assassinated before it could start.[64] However, the campaign was made redundant by Burebista's overthrow and death in the same year, after which his Getae empire fragmented into four, later five, independent petty kingdoms. These were militarily far weaker, as Strabo assessed their combined military potential at just 40,000 armed men, and were often involved in internecine warfare.[65][66] The Geto-Dacians did not again become a threat to Roman hegemony in the lower Danube until the rise of Decebal 130 years later (86 AD).
Roman Principate (30 BC – 284 AD)[edit]
Augustan era (30 BC – 14 AD)[edit]
Once he had established himself as sole ruler of the Roman state in 30 BC, Caesar's grand-nephew and adopted son Augustus inaugurated a strategy of advancing the empire's south-eastern European border to the line of the Danube from the Alps, the Dinaric Alps and Macedonia. The primary objective was to increase strategic depth between the border and Italy and also to provide a major fluvial supply route between the Roman armies in the region.[67]
On the lower Danube, which was given priority over the upper Danube, this required the annexation of Moesia. The Romans' target was thus the tribes which inhabited Moesia, namely (from west to east) the Triballi, Moesi and those Getae who dwelt south of the Danube. The Bastarnae were also a target because they had recently subjugated the Triballi, whose territory lay on the southern bank of the Danube between the tributary rivers Utus (Vit) and Ciabrus (Tsibritsa), with their chief town at Oescus (Gigen, Bulgaria).[68] In addition, Augustus wanted to avenge the defeat of Gaius Antonius at Histria 32 years before and to recover the lost military standards. These were held in a powerful fortress called Genucla (Isaccea, near modern Tulcea, Romania, in the Danube Delta region), controlled by Zyraxes, the local Getan king.[69] The man selected for the task was Marcus Licinius Crassus, grandson of Crassus the triumvir and an experienced general at 33 years of age, who was appointed proconsul of Macedonia in 29 BC.[70]
The Bastarnae provided the casus belli by crossing the Haemus and attacking the Dentheletae, a Thracian tribe who were Roman allies. Crassus marched to the Dentheletae's assistance, but the Bastarnae host hastily withdrew over the Haemus at his approach. Crassus followed them closely into Moesia but they would not be drawn into battle, withdrawing beyond the Tsibritsa.[71] Crassus now turned his attention to the Moesi, his prime target. After a successful campaign which resulted in the submission of a substantial section of the Moesi, Crassus again sought out the Bastarnae. Discovering their location from some peace envoys they had sent to him, he lured them into battle near the Tsibritsa by a stratagem. Hiding his main body of troops in a wood, he stationed as bait a smaller vanguard in open ground before the wood. As expected, the Bastarnae attacked the vanguard in force, only to find themselves entangled in the full-scale pitched battle with the Romans that they had tried to avoid. The Bastarnae tried to retreat into the forest but were hampered by the wagon train carrying their women and children, as these could not move through the trees. Trapped into fighting to save their families, the Bastarnae were routed. Crassus personally killed their king, Deldo, in combat, a feat which qualified him for Rome's highest military honour, spolia opima, but Augustus refused to award it on a technicality.[Note 4] Thousands of fleeing Bastarnae perished, many asphyxiated in nearby woods by encircling fires set by the Romans, others drowned trying to swim across the Danube. Nevertheless, a substantial force dug themselves into a powerful hillfort. Crassus laid siege to fort, but had to enlist the assistance of Rholes, a Getan petty king, to dislodge them, for which service Rholes was granted the title of socius et amicus populi Romani ("ally and friend of the Roman people").[75]
The following year (28 BC), Crassus marched on Genucla. Zyraxes escaped with his treasure and fled over the Danube into Scythia to seek aid from the Bastarnae.[76] Before he was able to bring reinforcements, Genucla fell to a combined land and fluvial assault by the Romans.[69] The strategic result of Crassus' campaigns was the permanent annexation of Moesia by Rome.
About a decade later, in 10 BC,[30] the Bastarnae again clashed with Rome during Augustus' conquest of Pannonia (the bellum Pannonicum 14–9 BC). Inscription AE (1905) 14 records a campaign on the Hungarian Plain by the Augustan-era general Marcus Vinucius:
Marcus Vinucius...[patronymic], Consul [in 19 BC]...[various official titles], governor of Illyricum, the first [Roman general] to advance across the river Danube, defeated in battle and routed an army of Dacians and Basternae, and subjugated the Cotini, Osi,...[missing tribal name] and Anartii to the power of the emperor Augustus and of the people of Rome.
Most likely, the Bastarnae, in alliance with Dacians, were attempting to assist the hard-pressed Illyrian/Celtic tribes of Pannonia in their resistance to Rome.
1st and 2nd centuries[edit]
Parece que en los años finales del gobierno de Augusto, los Bastarnae hicieron las paces con Roma. La Res Gestae Divi Augusti ("Actos del divino Augusto", 14 d. C.), una inscripción encargada por Augusto para enumerar sus logros, afirma que recibió una embajada de los Bastarnae en busca de un tratado de amistad. [77] Parece que se concluyó un tratado y aparentemente demostró ser notablemente efectivo, ya que no se registran hostilidades con los Bastarnae en fuentes antiguas sobrevivientes hasta c. 175, unos 160 años después de que se tallara la inscripción de Augusto. Pero la evidencia sobreviviente de la historia de este período es tan escasa que no se puede excluir que los Bastarnae se enfrentaron con Roma durante ese período. [Nota 5] Los Bastarnae pueden haber estado involucrados en elDacian Wars of Domitian (86–88) and Trajan (101–102 and 105–106), since these took place in the lower Danube region and it is known that both sides were supported by neighbouring indigenous tribes.[original research?]
In the late 2nd century, the Historia Augusta mentions that in the rule of Marcus Aurelius (161–180), an alliance of lower Danube tribes including the Bastarnae, the Sarmatian Roxolani and the Costoboci took advantage of the emperor's difficulties on the upper Danube (the Marcomannic Wars) to invade Roman territory.[78]
3rd century[edit]
During the late 2nd century, the main ethnic change in the northern Black Sea region was the immigration, from the Vistula valley in the North, of the Goths and accompanying Germanic tribes such as the Taifali and the Hasdingi, a branch of the Vandal people. This migration was part of a series of major population movements in the European barbaricum (the Roman term for regions outside their empire). The Goths appear to have established a loose political hegemony over the existing tribes in the region.
Under the leadership of the Goths, a series of major invasions of the Roman empire were launched by a grand coalition of lower Danubian tribes from c. 238 onwards. The participation of the Bastarnae in these is likely but largely unspecified, due to Zosimus' and other chroniclers' tendency to lump all these tribes under the general term "Scythians" – meaning all the inhabitants of Scythia, rather than the specific Iranic-speaking people called the Scythians.[79] Thus, in 250–251, the Bastarnae were probably involved in the Gothic and Sarmatian invasions which culminated in the Roman defeat at the Battle of Abrittus and the slaying of Emperor Decius (251).[80]Este desastre fue el comienzo de la Crisis del Imperio Romano en el siglo III , un período de caos militar y económico. En este momento crítico, el ejército romano quedó paralizado por el estallido de una segunda pandemia de viruela , la plaga de Cipriano (251–70). Zosimus describe los efectos como incluso peores que la anterior plaga de Antonine (166-180), que probablemente mató al 15-30% de los habitantes del imperio. [81]
Aprovechando el desorden militar romano, un gran número de pueblos bárbaros invadieron gran parte del imperio. La alianza sarmato-gótica del bajo Danubio llevó a cabo importantes invasiones de la región de los Balcanes en 252, y en los períodos 253-258 y 260-268. [82] Los Peucini Bastarnae se mencionan específicamente en la invasión 267/268, cuando la coalición construyó una flota en el estuario del río Tyras ( Dniester). The Peucini Bastarnae would have been critical to this venture since, as coastal and delta dwellers, they would have had seafaring experience that the nomadic Sarmatians and Goths lacked. The barbarians sailed along the Black Sea coast to Tomis in Moesia Inferior, which they tried to take by assault without success. They then attacked the provincial capital Marcianopolis (Devnya, Bulgaria), also in vain. Sailing on through the Bosporus, the expedition laid siege to Thessalonica in Macedonia. Driven off by Roman forces, the coalition host moved overland into Thracia, where finally it was crushed by Emperor Claudius II (r. 268–270) at Naissus (269).[83]
Claudius II was the first of a sequence of military emperors (the so-called "Illyrian emperors" from their main ethnic origin) who restored order in the empire in the late 3rd century. These emperors followed a policy of large-scale resettlement within the empire of defeated barbarian tribes, granting them land in return for an obligation of military service much heavier than the usual conscription quota. The policy had the triple benefit, from the Roman point of view, of weakening the hostile tribe, repopulating the plague-ravaged frontier provinces (bringing their abandoned fields back into cultivation) and providing a pool of first-rate recruits for the army. It could also be popular with the barbarian prisoners, who were often delighted by the prospect of a land grant within the empire. In the 4th century, such communities were known as laeti.[84]
The emperor Probus (r. 276–282) is recorded as resettling 100,000 Bastarnae in Moesia, in addition to other peoples, including Goths, Gepids and Vandals. The Bastarnae are reported to have honoured their oath of allegiance to the emperor, while the other resettled peoples mutinied while Probus was distracted by usurpation attempts and ravaged the Danubian provinces far and wide.[40][85] A further massive transfer of Bastarnae was carried out by Emperor Diocletian (ruled 284–305) after he and his colleague Galerius defeated a coalition of Bastarnae and Carpi in 299.[86]
Later Roman empire (305 onwards)[edit]
The remaining transdanubian Bastarnae disappear into historical obscurity in the late empire. Neither of the main ancient sources for this period, Ammianus Marcellinus and Zosimus, mention the Bastarnae in their accounts of the 4th century, possibly implying the loss of their separate identity, presumably assimilated by the regional hegemons, the Goths. Such assimilation would have been facilitated if, as is possible, the Bastarnae spoke an East Germanic language closely related to Gothic. If the Bastarnae remained an identifiable group, it is highly likely that they participated in the vast Gothic-led migration, driven by Hunnic pressure, that was admitted into Moesia by Emperor Valens in 376 and eventually defeated and killed Valens at Adrianople in 378. Although Ammianus refers to the migrants collectively as "Goths", he states that, in addition, "Taifali and other tribes" were involved.[87]
However, after a gap of 150 years, there is a final mention of Bastarnae in the mid-5th century. In 451, the Hunnic leader Attila invaded Gaul with a large army which was ultimately routed at the Battle of Châlons by a Roman-led coalition under the general Aetius.[88] Attila's host, according to Jordanes, included contingents from the "innumerable tribes that had been brought under his sway".[89] This included the Bastarnae, according to the Gallic nobleman Sidonius Apollinaris.[90] However, E.A. Thompson argues that Sidonius' mention of Bastarnae at Chalons is probably false: his purpose was to write a panegyric and not a history, and Sidonius added some spurious names to the list of real participants (e.g. Burgundians, Sciri and Franks) for dramatic effect.[91]
See also[edit]
- Carpathian Tumuli culture
- Tiberius Plautius Silvanus Aelianus
- List of Germanic tribes
- List of Celtic tribes
Notes[edit]
- ^ The terms imposed on Philip V of Macedon in 196 BC were: (i) loss of all possessions outside Macedonia proper (Philip had previously ruled extensive territories in Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor); (ii) standing army limited to 5,000 men and no elephants; (iii) navy limited to 5 warships plus royal galley; (iv) reparation payment of 1,000 talents (c. 26 tonnes) of silver, equivalent then to c. 4 tonnes of gold. (In antiquity, silver was far more valuable than today: the gold/silver value ratio was c. 1:7, compared to c. 1:100 today); (v) prohibited from waging war outside his borders without the Roman Senate's permission[48]
- ^ The main ones were: Histria (Sinoe), Tomis, Callatis, Apollonia (Istria, Constanţa, Mangalia, Sozopol)[54]
- ^ There is controversy about whether the Getae were Dacian or Thracian speakers and whether those two languages were similar. Strabo claims that the Getae were Thracians.[56] He adds that the Dacians spoke the same language as the Getae.[57] This gave rise to the hypothesis that Thracian and Dacian were essentially the same language (the Daco-Thracian theory). But the modern linguist Vladimir Georgiev disputes that Dacian and Thracian were closely related for various reasons, especially that Dacian and Moesian town names commonly end with the suffix -DAVA, while towns in Thrace proper generally end in -PARA. According to Georgiev, the language spoken by the Getae should be classified as "Daco-Moesian" and regarded as quite distinct from Thracian.[58] Support for the Daco-Moesian theory can be found in Dio, who confirms that the Moesians and Getae on the south bank of the Danube were Dacians.[59] But the scant evidence available for these two extinct languages does not permit any firm conclusions. For the dividing-line between the two placename forms, see the following map (lower map, scroll down): members.tripod.com
- ^ Crassus' feat, as Roman commander, of killing the enemy leader in combat arguably entitled him to the highest honour a Roman soldier could gain: the spolia opima (literally: "bountiful spoils", but this term may be a corruption of spolia optima, "supreme spoils"), the right to hang the armour stripped from the enemy leader in the temple of Jupiter Feretrius in Rome, in emulation of the Founder of Rome Romulus, a privilege granted only twice previously. But Crassus was denied the honour by Augustus on the technicality that he was not commander-in-chief of Roman forces at the time, a position claimed by Augustus himself.[11] Augustus also forbade Crassus to accept the honorary title of imperator ("supreme commander") from his troops, traditional for victorious generals. Instead, Augustus claimed the title for himself (for the 7th time).[72][73] Finally, although Dio states that Crassus was voted a Triumph in Rome by the Senate, there is no evidence in inscriptions of that year (27 BC) that it was actually celebrated. After his return to Rome, Crassus disappears from the record altogether, both epigraphic and literary. This is highly unusual in a relatively well-documented period for a person of such distinction who was still only about 33 years old.[original research?] His tomb has not been found in the excavated Crassus family mausoleum in Rome. This official "air-brushing from history" may imply punitive internal exile to a remote location, similar to that inflicted on the contemporary poet, Ovid, who in AD 8, for an unknown offence, was ordered by Augustus to spend the rest of his life in Tomis (Constanţa) on the Black Sea. Ronald Syme points out the similarity of Crassus' removal from the official record with that of Cornelius Gallus, the contemporary disgraced governor of Egypt, who was recalled by Augustus for assuming inappropriate honours.[74]
- ^ The Julio-Claudian period and the subsequent Roman Civil War of 68–9 (until AD 69) is reasonably well-covered by Tacitus' Annales (although substantial parts are missing) and Historiae. But the loss of Tacitus' narrative for the entire Flavian period (69–96) and of Ammianus Marcellinus's continuation until 353, as well as of most of Dio Cassius's History (up to 229), leaves a massive gap in our knowledge of the political history of the early empire, which is only scantily filled by inferior chronicles such as the Historia Augusta, inscriptions and other evidence
References[edit]
- ^ a b c "Plutarch • Life of Aemilius". penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ a b c "Titus Livius (Livy), The History of Rome, Book 40, chapter 57". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ a b c "LacusCurtius • Strabo's Geography — Book VII Chapter 2". penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ a b c "Cornelius Tacitus, Germany and its Tribes, chapter 46". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ "Cassius Dio — Book 51". penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ a b "Zosimus, New History 1.71 – Livius". www.livius.org. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ Tarasov I.M. The Balts in the Migration Period. Veleti. // Аллея Науки, № 10 (26), Ноябрь, 2018. P. 258.
- ^ Щукин М.Б. На рубеже эр. СПб.: Фарн, 1994. С. 20.
- ^ "Polybius • Histories — Book 25". penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2018-08-12.
- ^ Köbler *bʰas
- ^ a b Dio LI.24.4
- ^ Batty (2008)
- ^ a b Trubačev INDOARICA в Северном Причерноморье, pp. 212–3
- ^ Procopius. Wars (VIII.I4, 22–30)
- ^ Shchukin (1989) 65-6, 71–2
- ^ Batty (2008) 248
- ^ a b c d Strabo VII.3.17
- ^ Babeş (1969) 195–218
- ^ a b c Batty (2008) 238
- ^ Pliny NH IV.81
- ^ Pliny NH IV.100
- ^ Ptolemy III.5.9
- ^ Barrington Plate 22
- ^ Shchukin (1990), p. 10.
- ^ Batty (2008), 243.
- ^ Batty (2008), 222.
- ^ a b c Batty (2008), 237.
- ^ Strabo VII.5.2
- ^ Polybius XXV.6.2
- ^ a b Almassy 2006, p. 253.
- ^ CAH Vol X 1996.
- ^ Année Epigraphique (1905) no. 14
- ^ a b Livy XL.57
- ^ a b Livy XL.58
- ^ Gaius Valerius Flaccus Argonautica VI.97
- ^ Batty (2008), 222. Cotto: cf. Cottius, king of the Alpine Salassi tribe and friend of Augustus, after whom were named the Alpes Cottiae Roman province; and the Cotini Celtic tribe of the northern Carpathians. Both probably derived from cotto- "old" or "crooked"). Faliyeyev (2007), entries 3806, 3890. Clondicus: cf. Klondyke, name of some places in Wales and Scotland. Teutagonus: tribal name Teutones, the god named Teutates.
- ^ Pliny NH IV.14
- ^ a b Tacitus G.46
- ^ Dio LI.23.3, 24.2
- ^ a b Zosimus I.34
- ^ cf. Historia Augusta Probus 18
- ^ a b Todd (2004) 23-4
- ^ Todd (2004) 23
- ^ Shchukin (1990, p. 10)
- ^ Mallory. EIEC. Page 657
- ^ Batty (2008) 237-9
- ^ Todd (2004) 26
- ^ Livy XXXIII.30
- ^ A Mocsy. Pannonia and Upper Moesia
- ^ Livy XLI.19
- ^ Livy XLI.23 and XLII.12-4
- ^ Livy XLV.19
- ^ Smith's Dictionary: Curio
- ^ Strabo VII.6.1
- ^ Smith's Dictionary: Lucullus
- ^ Strabo VII.3.2
- ^ Strabo VII.3.13
- ^ Vladimir Georgiev (Gheorghiev), Raporturile dintre limbile dacă, tracă şi frigiană, "Studii Clasice" Journal, II, 1960, 39–58.
- ^ Dio LI.22.6–7
- ^ Strabo VII.3.11–12
- ^ Dio XXXVIII.10.2
- ^ Dio XXXVIII.10.3 and LI.26.5
- ^ Crişan (1978) 118
- ^ Strabo VII.3.5
- ^ Strabo VII.3.11
- ^ Dio LI.26.1
- ^ Res Gestae 30
- ^ Ptolemy
- ^ a b Dio LI.26.5
- ^ Dio LI.23.2
- ^ Dio LI.23.5
- ^ Dio LI.25.2
- ^ CIL VI.873
- ^ Syme (1986) 271-2
- ^ Dio LI.24
- ^ Dio LI.26.6
- ^ Res Gestae Aug. 31
- ^ Historia Augusta Marcus Aurelius II.22
- ^ Wolfram (1988) 45
- ^ Wolfram (1988) 45–46
- ^ Zosimus I.16, 21
- ^ Zosimus I.16, 20, 21
- ^ Zosimus I.22-3
- ^ Jones (1964) 620
- ^ Historia Augusta Probus 18
- ^ Eutropius IX.25
- ^ Zosimus IV.104-7; 107
- ^ Jordanes 38–40
- ^ Jordanes 38
- ^ Sidonius Carmina 7.341
- ^ Thompson (1996) 149
Bibliography[edit]
Ancient[edit]
- Res Gestae Divi Augusti (c. 14 AD)
- Ammianus Marcellinus Res Gestae (c. 395 AD)
- Dio Cassius Roman History (c. 230 AD)
- Eutropius Historiae Romanae Breviarium (c. 360 AD)
- Anonymous Historia Augusta (c. 400 AD)
- Livy Ab urbe condita (c. 20 BC)
- Jordanes Getica (c. 550 AD)
- Pliny the Elder Naturalis Historia (c. 70 AD)
- Ptolemy Geographia (c. 140)
- Sextus Aurelius Victor De Caesaribus (c. 380 AD)
- Sidonius Apollinaris Carmina (late 5th century AD)
- Strabo Geographica (c. 10 AD)
- Tacitus Annales (c. 100 AD)
- Tacitus Germania (c. 100 AD)
- Zosimus Historia Nova (c. 500 AD)
Modern[edit]
- Babeş, Mircea: Noi date privind arheologia şi istoria bastarnilor in SCIV 20 (1969) 195–218
- Barrington (2000): Atlas of the Greek and Roman World
- Batty, Roger (2008): Rome and the Nomads: the Pontic-Danubian region in Antiquity
- Crişan, Ion (1978): Burebista and his Time
- Faliyeyev, Alexander (2007): Dictionary of Continental Celtic Placenames (online)
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2000): Roman Warfare
- Hussey, Joan Mervyn (1966). Cambridge Medieval History. CUP Archive. ISBN 0-5200-8511-6. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- Heather, Peter (1999). The Visigoths from the Migration Period to the Seventh Century: An Ethnographic Perspective. Boydell & Brewer. ISBN 1-8438-3033-7. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- Heather, Peter (2009): Empires and Barbarians
- Jones, A.H.M. (1964): Later Roman Empire
- Köbler, Gerhard (2000): Indo-Germanisches Wörterbuch (online)
- Müllenhoff, Karl (1887): Deutsche altertumskunde (vol. II)
- Shchukin, Mark (1989): Rome and the Barbarians in central and eastern Europe: 1st century BC – 1st century AD
- Thompson, E.A. (1996): The Huns
- Todd, Malcolm (2004): The early Germans
- O. N. Trubačev (1999): INDOARICA в Северном Причерноморье
- Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2006). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase Publishing. ISBN 1-4381-2918-1. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- Wolfram, Herwig (1988): History of the Goths
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bastarnae. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Bastarnae . |